Overview
This workshop is designed to be run on your own computer. First, you need to download the data we use in the workshop. Then, you need to set up your computer by installing the software needed to analyze and process geospatial data.
Instructions are provided for installing all software on Windows, macOS, and Linux systems.
Workshop participants who use Docker and wish to use a Docker image made for the workshop will find advanced Docker installation instructions below.
Data
You can download all of the data used in this workshop by clicking this download link. The file is 58 MB.
The data will download as a single compressed (.zip) file.
Expand/unzip this file so that the data folder is on your
desktop or another convenient location.
For a full description of the data used in this workshop see the data page.
Software Installation
The table below summarizes all the software that must be installed for the workshop. Below the table we provide detailed instructions for installing each software for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
At points, the instructions assume some familiarity with the software installation process. As there are many different operating systems and environments, the installation on your computer may vary from the instructions.
| Install | Description | Website | Available for |
|---|---|---|---|
| R | free software environment for statistical computing and graphics. | r-project.org | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| RStudio | free integrated development environment (IDE) for the R programming language | rstudio.com | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| GDAL | Geospatial model for reading and writing a variety of formats | gdal.org | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| GEOS | Geometry models and operations | trac.osgeo.org/geos | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| PROJ.4 | Coordinate reference system transformations | proj4.org | Windows, macOS, Linux |
| UDUNITS | Unit conversions | unidata.ucar.edu/software/udunits/ | Windows, macOS, Linux |
R
Participants who do not already have R installed should download and install it.
Windows
To install R, Windows users should navigate to the CRAN download page and click
Download R for Windows. Click thebasesubdirectory.Clicking on
Download R 4.x.x for Windowswill download an.exeexecutable installer. Run the installer. The installer will guide you through the remaining steps.
macOS
To install R, macOS users should navigate to the CRAN download page and click
Download R for (Mac) OS X.A
.pkgfile containing the necessary components of base R can be downloaded by clicking on the first available link (this will be the most recent), which will readR-4.x.x.pkg.When the file finishes downloading, double click it to run the installer. The installer will guide you through the remaining steps.
Linux
Most Linux users can install R using the package management software on their computer. R is a part of many linux distributions and may already be installed.
Linux users can also click “Download R for Linux” from the CRAN download page. Instructions for a number of different Linux distributions are available.
RStudio
RStudio is a GUI for using R. Participants who do not already have R installed should download and install it.
Windows
Navigate to the RStudio download page. Download the executable (
.exe) installer by clicking the button labeledDownload RStudio for Windows. Run the installer. The installer will guide you through the remaining steps.
macOS
From the RStudio download page, download the disk image (
.dmg) installer by clicking the button labeledDownload RStudio for mac. Mount the disk image by double clicking it and drag RStudio to your applications directory.
Linux
Most Linux users can install RStudio using the package management software on their computer.
The RStudio download page has installers for some of the most popular Linux distributions.
GDAL, GEOS, and PROJ.4
The installation of the geospatial libraries GDAL, GEOS, and PROJ.4
varies significantly based on operating system.
These are all dependencies for sf,
the R package that we will be using for spatial data operations throughout this workshop.
Windows
Windows users should install the latest version of
Rtools.Navigate to the CRAN page for Rtools and download the appropriate
.exeexecutable installer.Follow the instructions on the page to add Rtools to your PATH.
macOS - Install with Packages (Beginner)
The simplest way to install these geospatial libraries is to install the latest version of Kyng Chaos’s pre-built package for GDAL Complete. Be aware that several other libraries are also installed, including the UnixImageIO, SQLite3, and NumPy.
After downloading the package in the link above, you will need to double-click the cardbord box icon to complete the installation. Depending on your security settings, you may get an error message about “unidentified developers”. You can enable the installation by following these instructions for installing programs from unidentified developers.
macOS - Install with Homebrew (Advanced)
Alternatively, participants who are comfortable with the command line can install the geospatial libraries individually using homebrew:
$ brew tap osgeo/osgeo4mac && brew tap --repair $ brew install proj $ brew install geos $ brew install gdal2
Linux
Steps for installing the geospatial libraries will vary based on which form of Linux you are using. These instructions are adapted from the sf package’s README.
Users who already have QGIS installed may find that all the geospatial packages are installed already. You can confirm and update specific packages in your system’s package manager.
For Ubuntu:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntugis $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install libgdal-dev libgeos-dev libproj-devFor Fedora:
$ sudo dnf install gdal-devel proj-devel proj-epsg proj-nad geos-develFor Arch:
$ pacman -S gdal proj geosFor Debian: The rocker geospatial Dockerfiles may be helpful. Ubuntu Dockerfiles are found here. These may be helpful to get an idea of the commands needed to install the necessary dependencies.
UDUNITS
Linux users will have to install UDUNITS separately.
Like the geospatial libraries discussed above, this is a dependency for the R package sf.
Due to conflicts, it does not install properly on Linux machines when installed as part of the sf installation process.
It is therefore necessary to install it using the command line ahead of time.
Linux
Steps for installing the geospatial will vary based on which form of Linux you are using. These instructions are adapted from the sf package’s README.
For Ubuntu:
$ sudo apt-get install libudunits2-devFor Fedora:
$ sudo dnf install udunits2-develFor Arch:
$ pacaur/yaourt/whatever -S udunitsFor Debian:
$ sudo apt-get install -y libudunits2-dev
R Packages
R Packages are collections of functions and reproducible code. The packages here will be used in the worshop and must be installed:
macOS users may be prompted to install Xcode Developer tools. Follow the prompt to install the Xcode or install it from the Mac App Store before continuing.
To install these packages in RStudio:
1. Open RStudio. You should see something like this:
2. Type the following text into the console and hit Return/Enter.
install.packages(c("dplyr", "ggplot2", "raster", "rgdal", "rasterVis", "sf"))
You should see a status message starting with:
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/bin/macosx/el-capitan/contrib/3.5/dplyr_0.7.6.tgz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 5686536 bytes (5.4 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 5.4 MB
trying URL 'https://cran.rstudio.com/bin/macosx/el-capitan/contrib/3.5/ggplot2_3.0.0.tgz'
Content type 'application/x-gzip' length 3577658 bytes (3.4 MB)
==================================================
downloaded 3.4 MB
When the installation is complete, you will see a status message like:
The downloaded binary packages are in
/var/folders/7g/r8_n81y534z0vy5hxc6dx1t00000gn/T//RtmpJECKXM/downloaded_packages
You are now ready for the workshop!
Docker Installation (Advanced)
Use this advanced option only if you are familiar with Docker and using Docker Images. If you are having trouble with option A, please contact the workshop organizers.
Docker provides developers with a means for creating interactive containers that contain pre-installed software. A selection of pre-installed software in Docker is called an image. An image can be downloaded and used to create a local container, allowing end-users to get software up and running quickly. This is particularly useful when a local installation of the software could be complex and time consuming. For R users, a Docker image can be used to create a virtual installation of R and RStudio that can be run through your web browser.
This option involves downloading an Docker image that contains an installation of R, RStudio Server, all of the necessary dependencies listed above, and almost all of the R packages used in the geospatial lessons. You will need to install the appropriate version of Docker’s Community Edition software and then download and use the rocker/geospatial Docker image to create a container that will allow you to use R, RStudio, and all the required GIS tools without installing any of them locally.
Once up and running - you’ll have full access to RStudio right from your browser:
Please be aware that the R package rasterVis is not included in the rocker/geospatial Docker image. If your instructor teaches with this package then you will need to install this R package yourself. All other R packages will already be installed for you.
Downloading and Installing Docker Community Edition
To get started with Docker, download the Docker Community Edition from Docker’s store. Community editions are available for Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems including Debian, Fedora, and Ubuntu.
The download pages for each of these operating systems contain notes about some necessary system requirements and other pre-requisites. Once you download the installer and follow the on-screen prompts.
Additional installation notes are available in Docker’s documentation for each of these operating systems: Windows, macOS, Debian, Fedora, and Ubuntu.
Using the
rocker/geospatialDocker Image via the Command LineDownload and Set-up
Once Docker is installed and up and running, you will need to open your computer’s command line terminal. We’ll use the terminal to download
rocker/geospatial, a pre-made Docker image that contains an installation of R, RStudio Server, all of the necessary dependencies, and all but one of the R packages needed for this workshop.You need to have already installed Docker Community Edition (see instructions above) before proceeding. Once you have Docker downloaded and installed, make sure Docker is running and then enter the following command into the terminal to download the
rocker/geospatialimage:$ docker pull rocker/geospatialOnce the pull command is executed, the image needs to be run to become accessible as a container. In the following example, the image is named
rocker/geospatialand the container is namedgis. The image contains the software you’ve downloaded, and the container is the run-time instance of that image. New Docker users should need only one named container per image.When
docker runis used, you can specify a folder on your computer to become accessible inside your RStudio Server instance. The followingdocker runcommand exposes Jane’sGitHubdirectory to RStudio Server. Enter the file path where your workshop resources and data are stored:$ docker run -d -P --name gis -v /Users/jane/GitHub:/home/rstudio/GitHub -e PASSWORD=mypass rocker/geospatialWhen she opens her RStudio instance below, she will see a
GitHubfolder in her file tab in the lower righthand corner of the screen. Windows and Linux users will have to adapt the file path above to follow the standards of their operating systems. More details are available on rocker’s Wiki.The last step before launching your container in a browser is to identify the port that your Docker container is running in:
$ docker port gisAn output, for example, of
8787/tcp -> 0.0.0.0:32768would indicate that you should point your browser tohttp://localhost:32768/. If prompted, enterrstudiofor the username and the password provided in thedocker runcommand above (mypassin the example above).Stopping a Container
When you are done with a Docker session, make sure all of your files are saved locally on your computer before closing your browser and Docker. Once you have ensured all of your files are available (they should be saved at the file path designated in
docker runabove), you can stop your Docker container in the terminal:$ docker stop gisRe-starting a Container
Once a container has been named and created, you cannot create a container with the same name again using
docker run. Instead, you can restart it:$ docker start gisIf you cannot remember the name of the container you created, you can use the following command to print a list of all named containers:
$ docker ps -aIf you are returning to a session after stopping Docker itself, make sure Docker is running again before re-starting your container!
Using the
rocker/geospatialDocker Image via KitematicDownload and Install Kitematic
Kitematic is the GUI, currently in beta, that Docker has built for accessing images and containers on Windows, macOS, and Ubuntu. You can download the appropriate installer files from Kitematic’s GitHub release page. You need to have already installed Docker Community Edition (see instructions above) before installing Kitematic!
Opening a Container with Kitematic
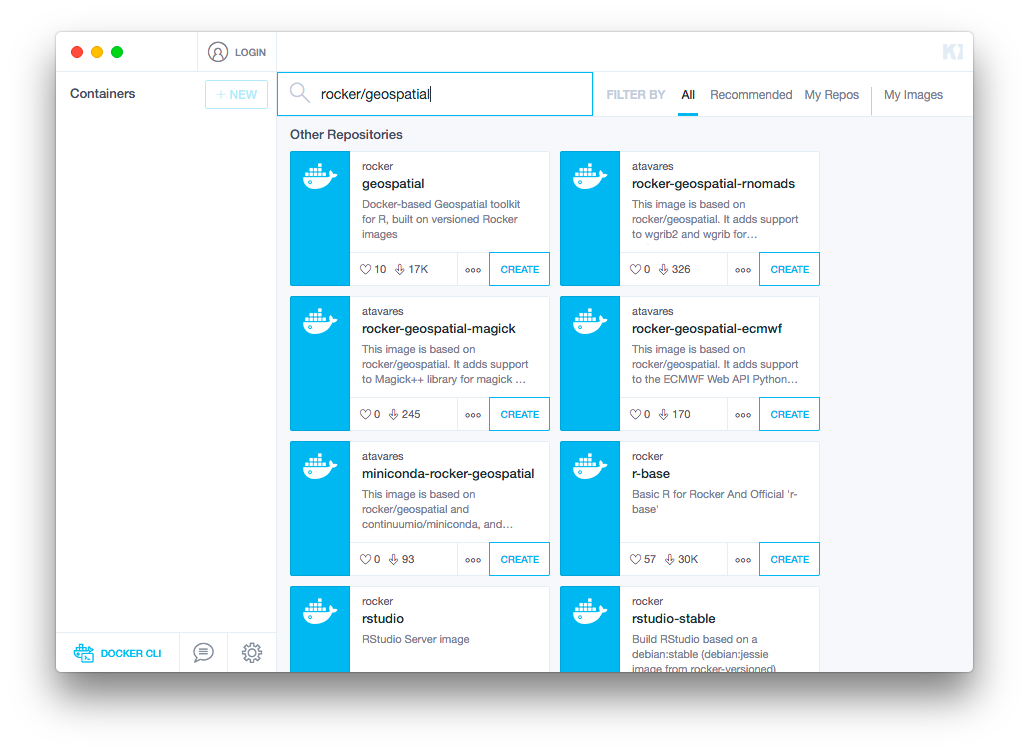
Once you have installed Kitematic, make sure the Docker application is running and then open Kitematic. You should not need to create a login to use Kitematic. If prompted for login credentials, there is an option to skip that step. Use the search bar in the main window to find
rocker/geospatial(pictured below) and clickCreateunder that Docker repository.
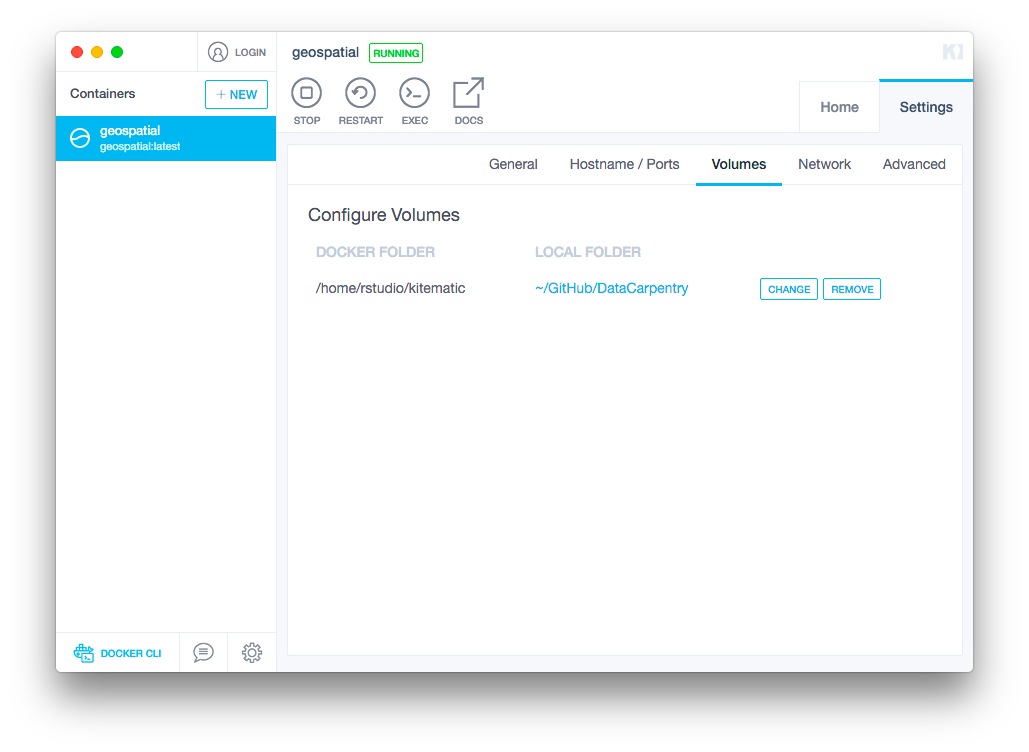
After downloading and installing the image, your container should start automatically. Before opening your browser, connect your Docker image to a local folder where you have your workshop resources stored by clicking on the
Settingstab and then choosingVolumes. ClickChangeand then select the directory you would like to connect to.
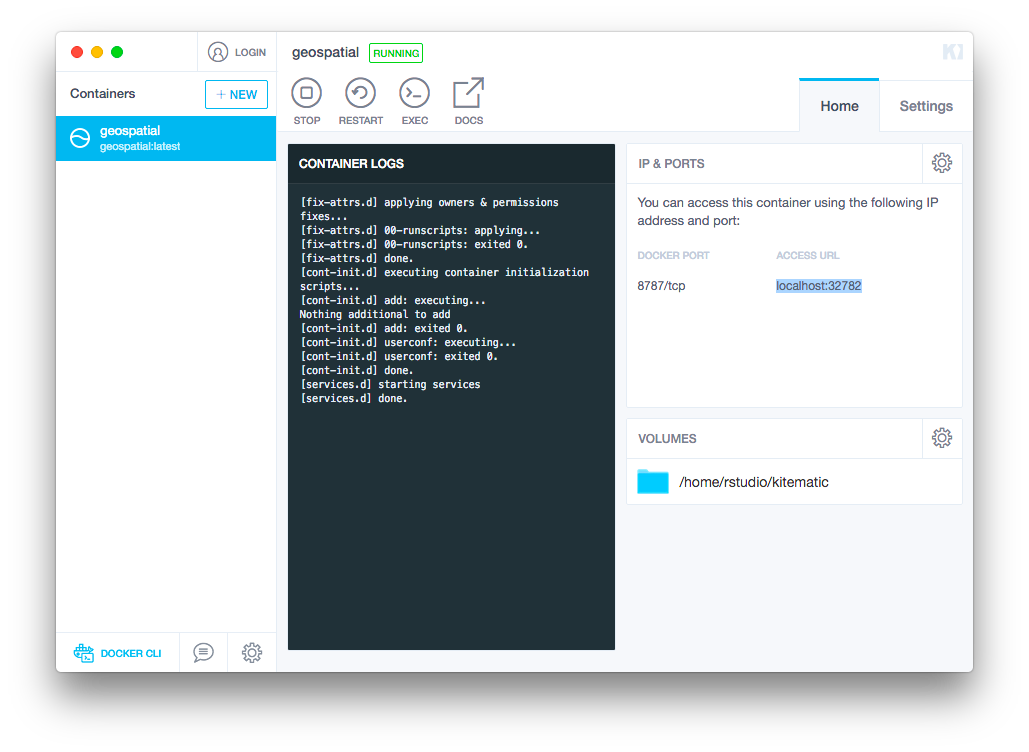
When you open RStudio instance below, you will see the contents of the connected folder inside the
kitematicdirectory in the file tab located in the lower righthand corner of the screen.When you are ready, copy the
Access URLfrom theHometab:
Paste that url into your browser and, if prompted, enter
rstudiofor both the username and the password.Stopping and Restarting a Container
When you are done with a Docker session, make sure all of your files are saved locally on your computer before closing your browser and Docker. Once you have ensured all of your files are available (they should be saved at the file path designated in
docker runabove), you can stop your Docker container by clicking on theStopicon in Kitematic’s toolbar.You can restart your container later by clicking the
Restartbutton.
Managing Docker Containers and Images
To obtain a list of all of your current Docker containers:
$ docker ps -aTo list all of the currently downloaded Docker images:
$ docker images -aThese images can take up system resources, and if you’d like to remove them, you can use the
docker prunecommand. To remove any Docker resources not affiliated with a container listed underdocker ps -a:$ docker system pruneTo remove all Docker resources, including currently named containers:
$ docker system prune -a
You are now ready for the workshop!